Structure, MOA, uses of warfarin
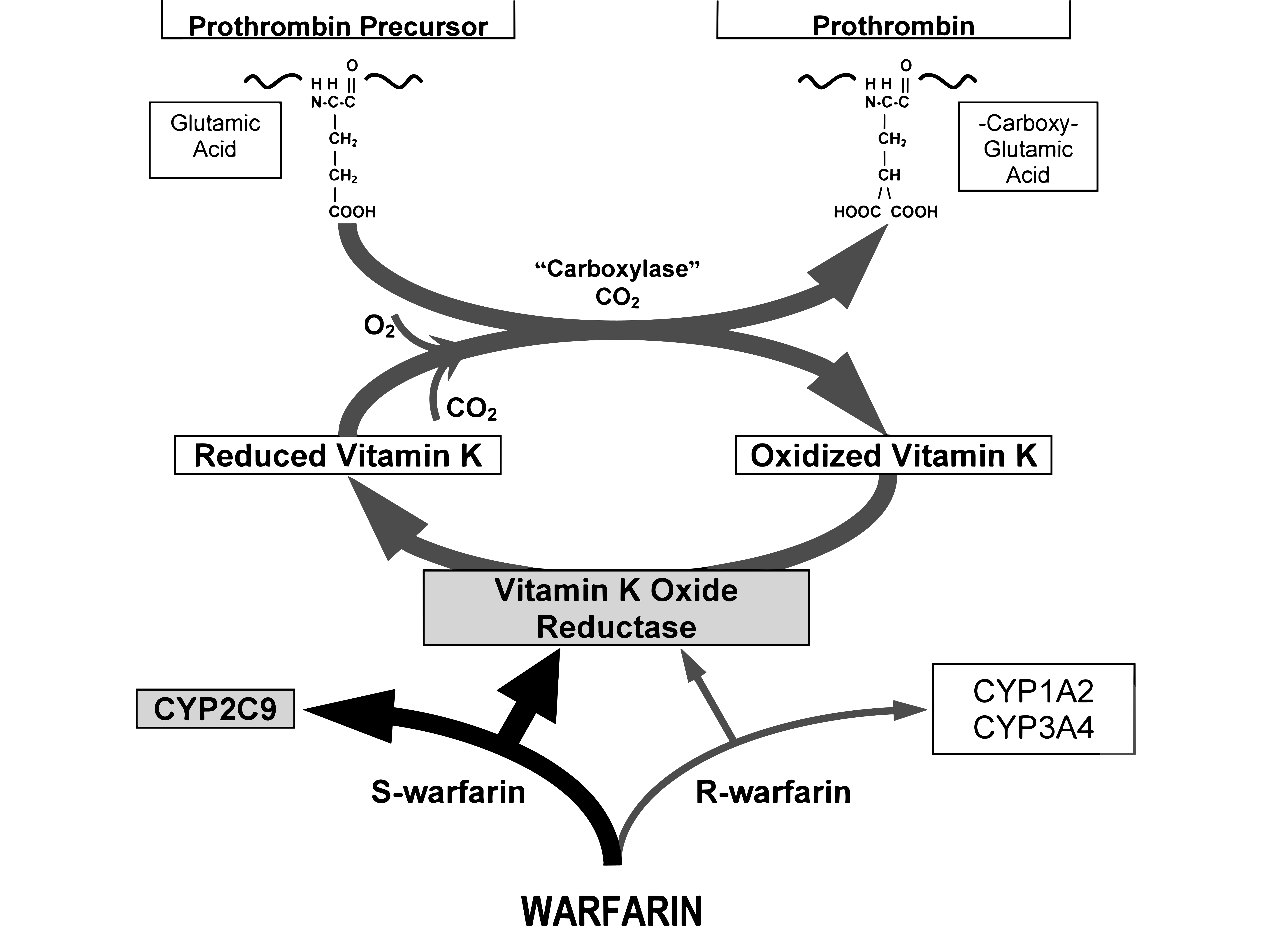
Warfarin is a type of anticoagulant known as a Vitamin K antagonist.
Here’s how it works:
Inhibition of Vitamin K: Warfarin inhibits the production of reduced from of Vitamin K by blocking the action of an enzyme called Vitamin K oxide reductase.
Impact on Clotting Factors: The reduced form of Vitamin K, Vitamin KH2, is a cofactor used in the γ-carboxylation of coagulation factors VII, IX, X, and thrombin. Without sufficient active Vitamin K1, these clotting factors have decreased clotting ability.
Resulting Anticoagulant Effect: By inhibiting the reactivation of Vitamin K, Warfarin decreases the synthesis of these clotting factors in the liver, thereby reducing the blood’s ability to clot.
USES of WARFARIN -
- Venous Thromboembolism
- Treatment of Myocardial infraction
- Ischemic Attacks
- Pulmonary embolism




Comments
Post a Comment